Pregnancy is the carrying of one or more offspring, known as a fetus or embryo, in the womb of a woman. In a pregnancy, there can be multiple gestations, as in the case of twins or triplets. Childbirth usually occurs about 38 weeks after conception; in women who have a menstrual cycle length of four weeks, this is approximately 40 weeks from the last normal menstrual period (LNMP). The World Health Organization defines normal term for delivery as between 37 weeks and 42 weeks. Human pregnancy is the most studied of all mammalian pregnancies.
One scientific term for the state of pregnancy is gravidity (adjective "gravid"), latin for “heavy” and a pregnant female is sometimes referred to as a gravida.[1] Similarly, the term parity (abbreviated as “para”) is used for the number of previous successful live births. Medically, a woman who has never been pregnant is referred to as a “nulligravida”, a woman who is (or has been only) pregnant for the first time as a “primigravida”, and a woman in subsequent pregnancies as a multigravida or “multiparous.” Hence, during a second pregnancy a woman would be described as “gravida 2, para 1” and upon live delivery as “gravida 2, para 2.” An in-progress pregnancy, as well as abortions, miscarriages, or stillbirths account for parity values being less than the gravida number. In the case of twins, triplets etc., gravida number and parity value are increased by one only. Women who have never carried a pregnancy achieving more than 20 weeks of gestation age are referred to as “nulliparous.”
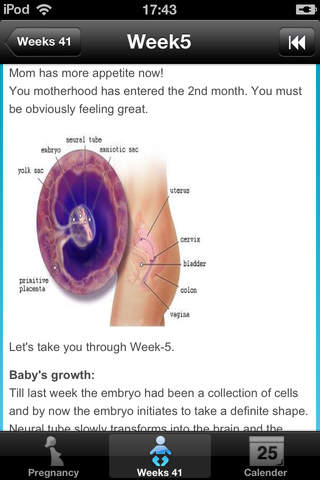
The term embryo is used to describe the developing offspring during the first 8 weeks following conception, and the term fetus is used from about 2 months of development until birth.